
150+ 2018 Google Ranking Factors to get to #1 spot!
If your a serious marketer, SEO Agency or handle your own website, here is a long list of 150+ 2018 Google Ranking factors to help your website get to the top of the Google SERPs.
Getting a website made is not enough to get you noticed by your target audience. You also have to work towards making your site noticed and ranked by Google. When your site will start appearing in SERPs, then only will you get your desired site traffic.
If you do not work towards enhancing your site visibility on SERPs, your competitors may go even more ahead of you and you might have to put in double the efforts in covering the gap. There might be many negative impacts on your business as well, like:
- Not many people may know about your business. Thus your users may not increase.
- Your goal of getting increased sales may not be fulfilled because when a user will search for something on Google, your site will not appear.
- If your site is not being ranked, you will not be in the competition. Thus your business may stand still at the same place for a long time.
- No matter how good offers or discounts you are willing to give in your business if your website doesn’t rank it will all go to waste because no one will know about it.
- If this situation continues and you are not getting any sale increase, you may have to shut down your business.
There’s no point getting a website made and just sitting back and waiting for users to come to you own their own.
You also have to work towards increasing the visibility of your site. You have to work on the following factors to get your site on the top of the Google search page ranking:
- Site Level Factors
- Backlink Factors
- Brand Signals
- Page-Level Factors
- Domain Factors
- User Interaction
- Special Algorithm Rules
- Social Signals
- On-Site WebSpam Factors
- Off Page WebSpam Factors
We will be discussing more about these factors in our article in detail.
Site Level Factors
- Domain Trust/TrustRank: The closer your site is to a highly-trusted seed site, the better your page ranking.
- Server Location: Depending on where the site is viewed, server location may influence page rankings. Especially true for geo-specific searches.
- Site Architecture: Google can better organize content category and theme of a well-built website.
- Site Uptime: Frequent downtimes or site maintenance can negatively influence site ranking.
- SSL Certificate: The usage of HTTPS is a ranking factor and having an SSL certificate helps boost page ranking. Crome Browser now actually blocks sites now without an SSL and tells users your site is no longer secure.
- Content Provides Value and Unique Insights: Content with little value or does not provide anything new or useful risk a decline in rankings.
- Presence of Sitemap: Having a sitemap improves page visibility since search engines can search pages more thoroughly.
- Thin Content Pages: Pages that have mostly images will not rank as well as Google cannot properly determine the topic of the page.
- Mobile Optimized: Sites that are mobile friendly are more likely to be recommended by Google than those that are not.
- Duplicate Meta Information On-Site: Duplicate meta information reduces page visibility.
- YouTube: YouTube videos are preferred in the search results.
- Breadcrumb Navigation: Very user-friendly and helps users and search engines know exactly where they are on a site.
- Contact Us Page: Google prefers sites with appropriate amounts of contact information. Preferably contact information that matches the whois info. This information should also match your citations.
- Terms of Service and Privacy Pages: Google prefers sites with these pages as they indicate that a site is trustworthy.
- User reviews/Site reputation: Sites with more positive reviews are more likely to be recommended by Google and improves page ranking.
- Number of Pages: A large site can distinguish itself from thin affiliate sites.
- Use of Google Analytics and Google Webmaster Tools: Having these programs in your site can influence page rank by improving page indexing.
- Site Usability: Sites that are not user-friendly negatively influences page ranking.
- Site Updates: A frequently updated site indicates fresh content, which is more likely to be recommended by Google.
Backlink Factors
- Natural Link Profile: Sites with natural link profiles are ranked higher.
- The diversity of Link Types: Link diversity indicates a natural link profile. Single source links are more likely to be considered as web spam.
- Positive Link Velocity: Sites with positive link velocity can get SERP boosts.
- Quality of Linking Content: Links from low-quality content gets less visibility than links from high-quality content.
- Links from 301: 301 redirects behave similarly to a direct link despite losing a bit of visibility.
- Social Shares of Referring Page: Page shares can influence a page’s ranking.
- Number of linking pages: Amount of linking pages influences page ranking

- User Generated Content Links: Google is able to distinguish links generated from user generated content and the site owner.
- Link Title Attribution: Link titles can give small amounts of relevancy.
- Link Location In Content: Links at the beginning of content carries more weight than ones at the end of the content.
- Keyword in Title: Links that contains a page’s keywords is more likely to be recommended by Google.
- Word Count of Linking Content: Links from a long post is more valuable than a link from a small post.
- Contextual Links: Links found within a page’s content is more powerful than a link found on an empty page or elsewhere.
- Linking Domain Relevancy: Links from a completely unrelated site is not as valuable as a link from a similar niche.
- Guest Posts: While valuable, may not be as important as a contextual link on the same page.
- Authority of Linking Page: Greatly influences page ranks.
- Links from Bad Neighbourhoods: Links from bad neighborhoods negatively influence page rank.
- Sitewide Links: Sitewide links only count as a single link.
- Links from .edu and .gov Domains: While it doesn’t affect the importance of the site, it can be influenced by SEO algorithms
- Alt Tag (for Image Links): It functions similarly to an anchor text and can improve visibility.
- “Sponsored Links” Or Other Words Around Link: Having “sponsors” or anything similar can decrease the value of a link.
- Text Around Link Sentiment: Links with positive sentiments more likely carry more weight.
- Internal Link Anchor Text: Another way to increase relevancy, but is likely to be weighed differently than backlink anchor text.
- Backlink Anchor Text: While not as important as it used to be, anchor text still provides relevancy when used in small amounts.
- Reciprocal Links: Excessive Link Schemes negatively influences page rank.
- TrustRank of Linking Site: Trustworthiness of sites linking to your page determines your “TrustRank”.
- The number of Outbound Links on Page: Links with more outbound links gets less page rank than a page with fewer outbound links.
- Links From Competitors: Links from other pages may be more valuable for a particular keyword. Especially within the SERP.
- PBN’s (Private Blog Networks): Although frowned upon by Google, PBN’s are basically paid or made links on expired domains that are bought for their previous rank and traffic and now used to link out and pass their “juice”.
- Authority of Linking Domain: A domain with higher authority performs better than one with a lower authority.
- Links from “Hub” Pages: Links from pages that are considered as top resources for a particular topic is given increased visibility.
- Linked to as Wikipedia Source: Links from Wikipedia are considered trustworthy and authoritative by search engines despite being nofollow links.
- Citations: On the local level citations are very important to local rankings. Citations are basically your NAP (Name, Address, and Phone number) listed on large sites typically directories like Yellow Pages, Yelp and Google Places.
- Link from Authority Sites: Links from an authority site has better visibility than a niche site.
- Links to Homepage Domain that Page Sits On: A link’s weight can be influenced by links referring to the page’s homepage.
- Linking Domain Age: Aged domains have more powerful backlinks than newer ones.
- Nofollow Links: Google doesn’t generally follow them, but nofollow links may still be able to influence rankings.
- Forum Profile Links: Google potentially devalues links from forum profiles due to spamming.
- Links from Real Sites vs. Splogs: Google gives more weight to “real sites” compared to fake blogs. They are distinguished by using brand and user-interaction signals.
- Excessive 301 Redirects to Page: 301 redirects risks decrease in page rank.
- Co-Occurrences: Words appearing around backlinks helps Google categorize your page.
- Link Location on Page: Links in a page’s content are more powerful than ones placed at the sidebar or footer area.
- The number of Linking Root Domains: Having more linking root domains can result in better page rankings.
- Negative Link Velocity: Negative link velocity is a sign of decreasing popularity, and as such, a decrease in page ranks.
- DMOZ Listed: DMOZ Listed sites are considered more trustworthy.
- Number of Links from Separate C-Class IPs: More links results in improved page rankings.
- Backlink Age: Older links have better ranking power than new backlinks.
- Country TLD of Referring Domain: Country specific TLD links can help increase page rank within that country.
- Page Level Relevancy: Links relevant to a page’s content is more valuable than a link from an unrelated page.
- org Microformats: Pages with micro formatting perform better than those without them.
Understanding all the 2018 Google Ranking factors is not always an easy task. SEO factors change often and most people dont always have the time
Brand Signals
- Co-Citations: Non-Hyperlinked brand mentions are usually considered by Google as brand signals.
- Brand Name Anchor Text: Branded anchor text significantly influences page rankings.
- The legitimacy of Social Media Accounts: Legitimate social media accounts play a significant role in page rankings.
- The number of RSS Subscribers: Since Google owns Feedburner RSS, they use the subscriber data as a ranking factor.
- Branded Searches: If a site is searched on Google, it takes that fact into consideration when determining a brand.
- Brick and Mortar Location with Google+ Local Listing: Since real businesses have offices, Google may use location data to determine the brand size of a site.
- The site has Twitter Profile with Followers: A Twitter profile with a lot of followers indicate a popular brand.
- Official Linkedin Company Page: Real businesses usually have a company Linkedin page.
- Site Has Facebook Page and Likes: Brands usually have Facebook pages with a lot of likes.
- Employees Listed at Linkedin: Linkedin profiles that indicate they work for a company is a ranking factor.
- Brand Mentions on News Sites: Big brands are often mentioned in Google News. Some brands even have their own Google News feed.
- Domain Registration Length: Legitimacy of a domain can be seen by how long it is registered for. Longer registration length indicates a more valuable domain.
Page-Level Factors
- Title Tag Starts with Keyword: Title tags that start with keywords perform better than keywords placed at other places in the title.
- Broken Links: Can indicate whether a site is neglected or abandoned, which can affect a site’s ranking.
- Page Category: Category of a page affects its relevancy. Pages that are more relevant to the category gets better visibility and vice versa.
- Rel=Canonical: Tells Google one URL is equivalent to another. Can prevent pages from being considered as duplicate content.
- Syndicated Content: Original content performs better than something that is copied from another source.
- Affiliate Links: Having too many affiliate links may result in Google focusing on the linked sites instead.
- H1 Tags: The use of this tells search engines what the main topic of the page is about and should include your keyword.
- Bullets and Numbered lists: Adding bullets and numbers make a page more user-friendly and is more likely to be recommended by Google.
- Keyword in Description Tag: Having keywords in a site description can increase site rankings.
- Reading Level: User reading level affects site rankings. Sites popular with users that have basic reading levels can potentially have better rankings.
- Date of Content Updates: Using Google Caffeine, Google favors how fresh a content of a website is, as denoted by a page’s update date.
- User-Friendly Layout: Making the main content of a page immediately visible increases site visibility and rankings.
- Page Age: Older pages that are regularly updated can outperform newer pages.
- Parked Domains: Parked domains have lower search visibility.
- Keyword Density: Keywords are used to determine a topic of a webpage, but using it too much can damage ranking and visibility.
- Duplicate Content: Having duplicate content on the site negatively affects site visibility.
- Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) Keywords: LSI extracts meaning with more than one meaning. As such, having LSI keywords can affect rankings.
- The magnitude of Content Updates: Adding or removing sections contributes more to content freshness compared to reordering words on a site.
- Content-Length: Longer content is more preferred than shorter ones, and increases visibility.
- Grammar and Spelling: Sites with proper grammar and spelling increases page visibility.
- HTML errors/W3C validation: Sites with bad coding is an indicator of a poor quality site, which can negatively affect rankings.
- Keyword in Title Tag: Aside from content, title tags is the most important content and greatly influences SEO.
- Keyword in H2 and H3 Tags: Keywords appearing as a subheading in H2 and H3 format can boost site relevancy.
- Human Editors: Human Editors can influence page results (unconfirmed).
- References and Sources: Putting references and sources on pages indicates a high-quality page, which helps boost page rank.
- Image Optimization: Images can affect page visibility depending on what is entered as their file name, title, alt text, caption, and description.
- Outbound Link Theme: Search engines may use content from linked sites for content relevancy.
- Keyword in H1 Tag: Keywords in H1 tags can boost site rankings.
- Helpful Supplementary Content: Having them can increase page rankings.
- URL Length: Long URL lengths can hurt page visibility.
- Historical Page Updates: How often a site is updated contributes to content freshness that affects rankings.
- LSI Keywords in Title and Description Tags: Having LSI keywords in the title and description of a page can affect rankings.
- URL String: Google reads the categories within the URL string and provides category visibility for a page.
- Multimedia: Having multimedia elements can increase content quality.
- Keyword in URL: Having a keyword in page URL can boost page rankings.
- Useful Content: Having useful content influences page ranking.
- Too Many Outbound links: Having too many links can distract users from a page’s main content.
- Number of Internal Links Pointing to Page: Page importance can be signified by the number of internal links it has.
- The number of Outbound Links: Excessive outbound links can hurt visibility.
- Page Loading Speed via HTML: How fast a page loads can affect a site’s ranking.
- Page Loading Speed via Chrome: How fast a page loads using Google Chrome can affect site rankings as it takes into account several other factors.
- The quantity of Other Keywords Page Ranks For: Ranking for several other keywords other than the main one indicates that a page has good quality,
- URL Path: Pages closer to the homepage has better authority.
- Keyword Prominence: Having a keyword appear at the beginning of a page’s content can significantly boost rankings.
- Quality of Internal Links Pointing to Page: Authoritative pages have better quality links compared to other lower quality pages.
- WordPress Tags: For WordPress sites, having tags that are WordPress specific can boost page relevancy.
- Priority of Page in Sitemap: Page priority within a sitemap can affect its ranking.
- Outbound Link Quality: Linking to authority sites can boost site rankings.
- Page’s PageRank: Pages with higher page ranks fare better than ones with lower ranks.
- Keyword Word Order: Exact matches of a keyword performs better than ones phrased differently.
- Page Host’s Domain Authority: Pages on an authoritative domain ranks higher than domains with less authority.
- A keyword is Most Frequently Used Phrase in Document: Keywords that appear often in a document can boost rankings.
Domain Factors
- Penalized WhoIs Owner: If a person has been reported or penalized in the past, their sites may be under Google’s surveillance. This can negatively affect rankings.
- Exact Match Domain (EMD): Very effective for high-quality websites, but low-quality sites risk ranking drops.
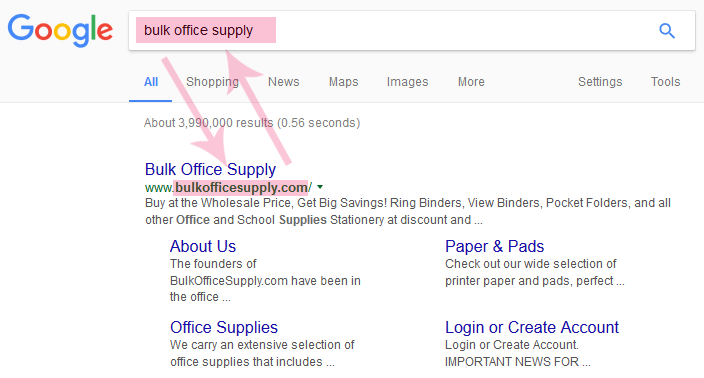
Example of EMD in effect. - Keywords in Top Level Domain: Keywords that appear in a domain name is made bold and can boost rankings.
- Public vs. Private WhoIs: WhoIs information that is set to private can be deemed suspicious and negatively affect site rankings.
- Domain Age: Is used, but not a large factor.
- Keyword in Subdomain Name: Rankings can be increased by having a keyword appearing in the subdomain.
- Keyword as First Word in Domain: Putting target keywords at the start of a domain significantly boosts ranking compared to having them in the middle or end.
- Domain History: If sites have unstable ownership or continuous drops, they risk Google invalidate any links pointing to the domain.
- Country Top Level Domain (TLD) extension: Helps boost rankings for a particular country, but global rank is limited. Sites that are in Canada should have a .ca extension but doing so also limits your global rank compared to .com
User Interaction
- Number of Comments: Pages with a lot of comments indicate high user interaction and quality site.
- Organic Click Through Rate (CTR) for a Keyword: Pages with increased CTR can improve SERP for a particular keyword.
- Repeat Traffic: Sites with repeat traffic can get Google ranking boosts.
- Direct Traffic: Google uses data from Google Chrome to determine site traffic. High direct traffic indicates high-quality sites.
- Organic CTR for All Keywords: Organic CTR is valuable for visibility.
- Blocked Sites: Feature is discontinued in Chrome, but is still used by Panda as a quality indicator.
- Chrome Bookmarks: Bookmarked pages can get ranking boosts since Google collects usage data from Chrome.
- Dwell Time: Indicates how long someone stays on your site after coming from a Google search. High dwell time implies good site quality.
- Google Toolbar Data: Toolbar data is used to determine to rank, but it is unknown what kind of data is gathered.
- Bounce Rate: Page bounce rate could be used by Google for page ranking. Pages where users quickly bounce implies low-quality pages.
Special Algorithm Rules
- Single Site Results for Brands: Several results from the same site can appear when searching for domain or brand-oriented keywords.
- Image Results: Organic listings for image results on Google Image Search are usually dismissed by Google.
- Google+ Circles: Higher results are given to sites and authors that are added to your Google Plus Circles. Having people in these circles are also your content gets shown in Google organic results.
- Shopping Results: Shopping results can be displayed in organic SERPs.
- Big Brand Preference: Brands are given ranking boosts for short-tail searches after the “Vince Update”.
- Local Searches: Local results are usually placed above the organic SERPs.
- User Search History: A search chain can influence results for later searches.
- User Browsing History: Sites frequently visited by users while signed into Google can get a SERP boost.
- DMCA Complaints: Pages with DMCA complaints are negatively impacted for page ranking.
- Safe Search: Adult content won’t appear for users with Safe Search turned on.
- Query Deserves Freshness: Newer pages are given a ranking boost for certain searches by Google.
- Query Deserves Diversity: Diversity can be added to a SERP for ambiguous keywords.
- Geo-Targeting: Preference is given to sites with local servers and country-specific domain name extensions.
- Domain Diversity: More domains are supposedly added to a SERP page after the “Bigfoot Update”.
- Google News Box: Certain keywords can trigger a Google News box.
- Easter Egg results: Google has a lot of Easter Egg results.
- Transactional Searches: Different results may appear for keywords related to shopping and transactions.
Social Signals
- Authority of Google+ User Accounts: +1’s from accounts with higher authority carries more weight than accounts with fewer followers.
- The number of Google +1’s: May have an influence on ranking factors despite statements saying otherwise.
- Pinterest Pins: Considering Pinterest’s popularity, Pinterest Pins can be considered a ranking factor.
- Number of Tweets: The number of tweets a page has can influence its page rank.
- Facebook Shares: Since they are similar to backlinks, shares have more influence than likes.
- Authority of Facebook User Accounts: Like Twitter, shares from a more influential account carries more weight.
- Site Level Social Signals: Search visibility of a site is influenced by site-wide social signals, which can affect its overall authority.
- Votes on Social Sharing Sites: Shares from other sites like Reddit and Digg are also taken into consideration for ranking factors.
- Social Signal Relevancy: Relevant information from accounts sharing page content and text surrounding the link is likely used by Google for page ranks.
- The number of Facebook Likes: The number of likes a page has can slightly influence its page ranking despite Google not being able to see most Facebook accounts.
- Authority of Twitter Users Accounts: Tweets from highly influential profiles like movie stars have a higher impact than less influential accounts.
- Known Authorship: Information tied to verified online profiles are ranked higher than content with no verification.
On-Site WebSpam Factors
- Panda Penalty: Panda penalizes content farms and sites that provide low-quality content. As a result, their search visibility is reduced.
- Links to Bad Neighbourhoods: Links to “bad neighborhoods” can negatively impact search visibility.
- Excess PageRank Sculpting: Nofollowing outbound links or most internal links may indicate system exploitation.
- Redirects: Cloaking severely penalizes a site. It also risks getting de-indexed.
- Meta Tag Spamming: If Google suspects you are exploiting the algorithm through keyword stuffing, the site may be penalized.
- IP Address Flagged as Spam: This may hurt the page ranking of the sites on your server.
- Autogenerated Content: Google does not favor autogenerated content. If suspected, can result in a penalty or de-indexing.
- Site Over-Optimization: Excessive keyword decoration and other on-page factors can damage page rankings.
- Ads Above the Fold: Sites with lots of ads above the fold is penalized by the Page Layout Algorithm.
- Page Over-Optimization: Unlike Panda, Penguin targets individual pages and can also damage page rankings.
- Popups or Distracting Ads: Popups and distracting ads are signs of a low-quality site, according to the official Google Rater Guidelines Document.
- Affiliate Sites: Google dislikes affiliate sites and may reduce search visibility of your site.
- Hiding Affiliate Links: Taking extreme measures to hide affiliate links can risk penalties to page rankings.
Off Page WebSpam Factors
- Link Profile with High Percentage of Low-Quality Links: Links from sources used by black hat SEO may indicate algorithm exploitation.
- Temporary Link Schemes: The act of creating and quickly removing spammy links. Will be penalized if caught.
- Selling Links: Doing this negatively impacts toolbar PageRank and reduces search visibility.
- Reconsideration Request: Can lift a penalty if successful.
- Unnatural Links Warning: Google warns sites of unnatural links before dropping their page ranks.
- Google Sandbox: Sites that receive a sudden influx of links are occasionally put in the Google Sandbox, which temporarily limits search visibility.
- “Poison” Anchor Text: Implies spam or a hacked site, which negatively impacts site ranking.
- Google Dance: This is Google’s method to determine whether a site is exploiting algorithms.
- Disavow Tool: Can remove a manual or algorithmic penalty for sites that received negative SEO.
- Manual Penalty: Google may sometimes hand out manual penalties.
- Penguin Penalty: If a site is hit by Google Penguin, their search visibility is greatly reduced.
- Linking Domain Relevancy: Penguin is more likely to target sites with suspicious numbers of links from unrelated sites.
- Unnatural Influx of Links: Phony links can penalize your site.
- Links from the Same Class C IP: Suspicious amounts of links from the same server IP may lead to getting penalized.
Hiring a website designer and an SEO expert are two completely different things. A website cannot rank without basic SEO services which not every web designer is well versed in. Web Design Plus can help you rank better on Google with its best and affordable SEO and Website Design Services.
We take care of all your requirements and business needs to give you the best possible results. Our professionals are well-trained in their work and they know how to provide the best possible solution for any given business needs.
You just have to give us your requirements and we will make sure the outcome is up to your expectations. We can also give SEO services that can help your site get a better ranking. We do proper keyword research and competitor research to know what is your current stand in the market. We then for our strategies accordingly.
Our services are available for all types of budgets. Our monthly packages start at $300 per month, that is undoubtedly cheaper than printing flyers, a newspaper ad or running Google Ads with no long-term results. We do offer smaller packages for those on a smaller budget but the results will be smaller. During the process, you have to be a little patient. SEO is a process that can not give instant results. It can take 1 week or 1-2 months for Google to pick up your site depending on the quality of SEO work done.
To get your site built or get your existing site on the top of SERPs, you can contact Web Design Plus on either of our numbers +1 (305) 677-9862 / +1 (888) 228-4521. You can also contact us on our email sales@webdesignplusseo.com for any query or details.
Google is the master of the internet making it hard to 100% guarantee anything. But we try our best to implement the best steps we can to increase the rank of your website. Google controls how it ranks a website. We will provide monthly reports of all our work so you can see our progress.



